At the heart of each of our custom packages lies an oil-free rotary-lobe compressor. The rotary-lobe compressor is a variant of a rotary-type positive displacement compressor.
Rotary-lobe compressors are typically known as ‘roots-type’ blowers or vacuum boosters, according to the situation in which they are used:
Since these machines are of the positive-displacement type, changes in gas properties do not greatly affect the inlet volumetric flow. Rotary-lobe compressors are simple to operate, requiring no surge control, pressurised lube oil systems, speed-reducing gearboxes, etc. Control of these machines is generally via transmitters, which are wired up to a junction box at the skid edge and communicate with the DCS. There is no need for a standalone PLC-based unit control panel.
If you would like more information, you can view our oil-free rotary-lobe gas compressors brochure.

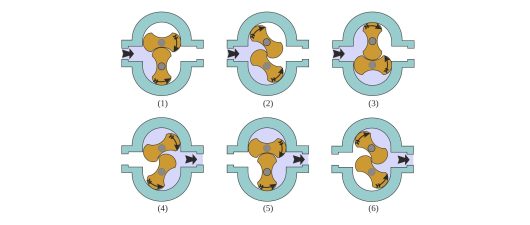
The rotary-lobe compressor incorporates two intermeshing rotors mounted on parallel shafts. In a twin-lobe compressor, each rotor has two lobes (four lobes per compressor). In a tri-lobe machine each rotor has three lobes (six lobes per compressor). Twin-lobe (bi-lobe) machines are normally used for process gas applications.
The rotary-lobe compressor was invented by two brothers, Philander Higley Roots and Frances Marion Roots, who patented their design in 1860.